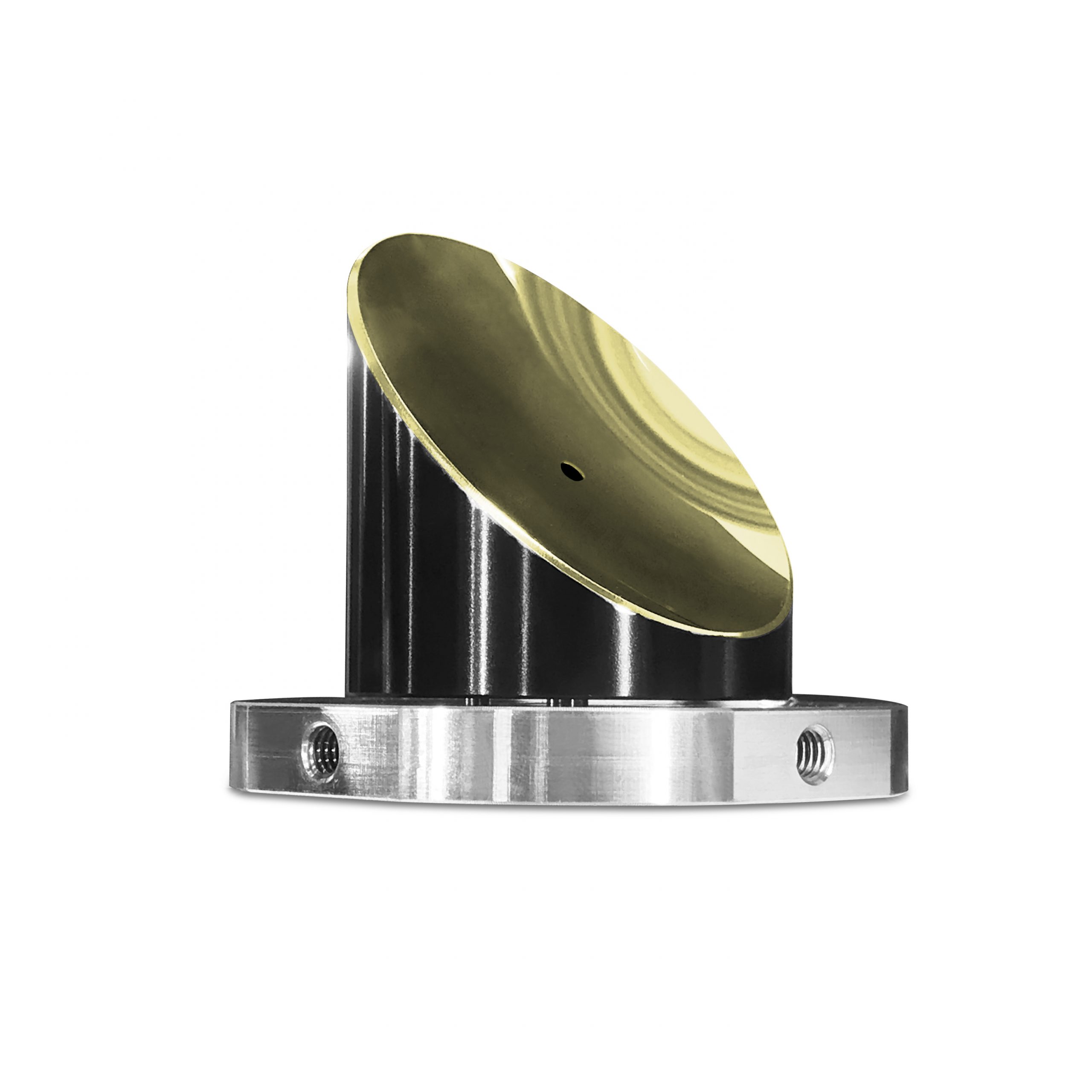
Order Sample OAP Mirror
- Diameter=25.4mm, Offaxis Angle=90°
- Coating: UV Enhance Aluminum
Off Axis Parabolic Mirror
An off-axis parabolic mirror (OAP) is a type of aspherical mirror that consists of a small section cut out from a larger, so-called “parent” parabolic mirror. OAP mirrors are designed to focus or collimate broadband light without introducing spherical aberration
Improved image quality: Off-axis parabolic mirrors have a larger field of view and produce sharper, distortion-free images with no spherical or coma aberration. They are therefore useful for applications that require high-quality imaging, such as astronomy, microscopy, and laser focusing.
Reduced astigmatism: Off-axis parabolic mirrors have a reduced amount of astigmatism compared to spherical mirrors. Astigmatism is an optical aberration that can cause images to appear distorted, particularly when viewing off-axis.
Compact design: Off-axis parabolic mirrors can be designed to be more compact than traditional parabolic mirrors, which require a larger size to achieve the same optical quality. This makes them useful in applications where space is limited, such as in telescopes or camera lenses.
Improved light collection: Off-axis parabolic mirrors can collect more light than spherical mirrors, especially when used with a detector or sensor that is located at the center of curvature. This makes them useful in applications where a high degree of light collection is important, such as in solar concentrators or laser beam steerin
An off-axis parabolic mirror (OAP) is a useful tool in optical design. It combines the achromatic and diffraction-limited imaging properties of a parabolic mirror with the ability to deviate the light path off-axis, which is useful for most imaging systems. However, when used improperly, OAPs can be difficult to align and achieve ideal imaging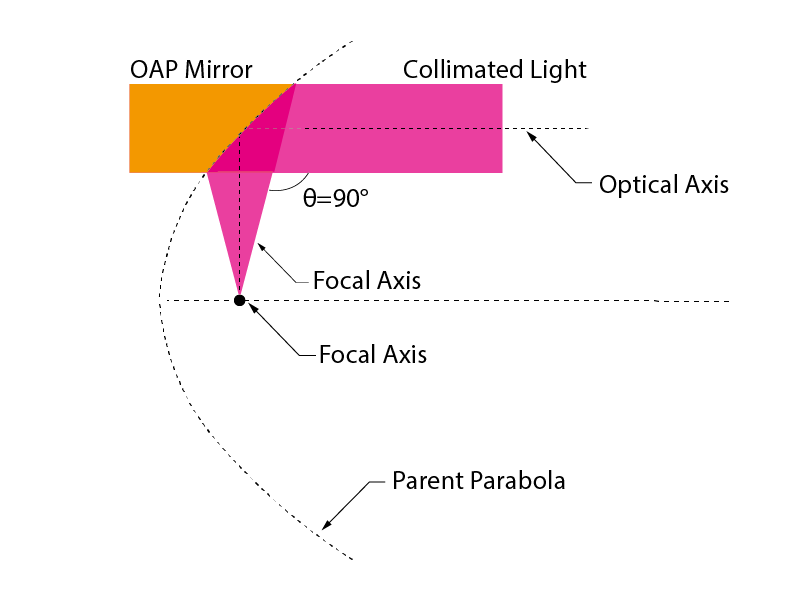 |
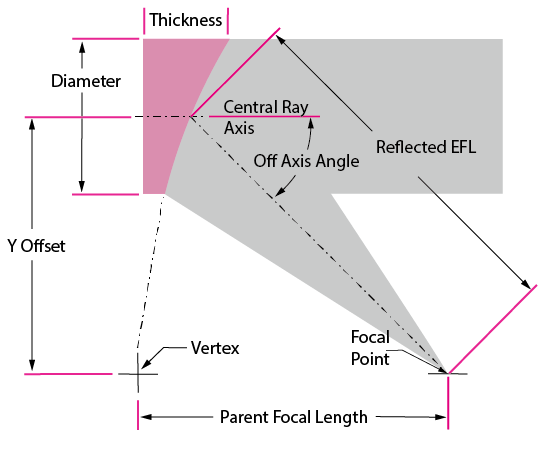
Advanatges of Offaxis Parabolic MirrorA parabolic mirror takes light from a point source located at the focus and creates a collimated beam. In other words, a source with spherical wavefronts placed at the parabolic focus is converted into a beam with plane wavefronts. The reverse operation is also true; plane wavefronts incident on the parabolic mirror are focused at the focal point. This is a valuable tool for optical design because the single surface of an OAP can produce a diffraction limited image without chromatic effects. A complete parabolic mirror would focus a collimated beam at its focal point, which is often not useful because it overlaps with part of the incoming beam. Accessing the focal point can be difficult and even impossible without obstructing part of the incoming beam. |
Common Specifications
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
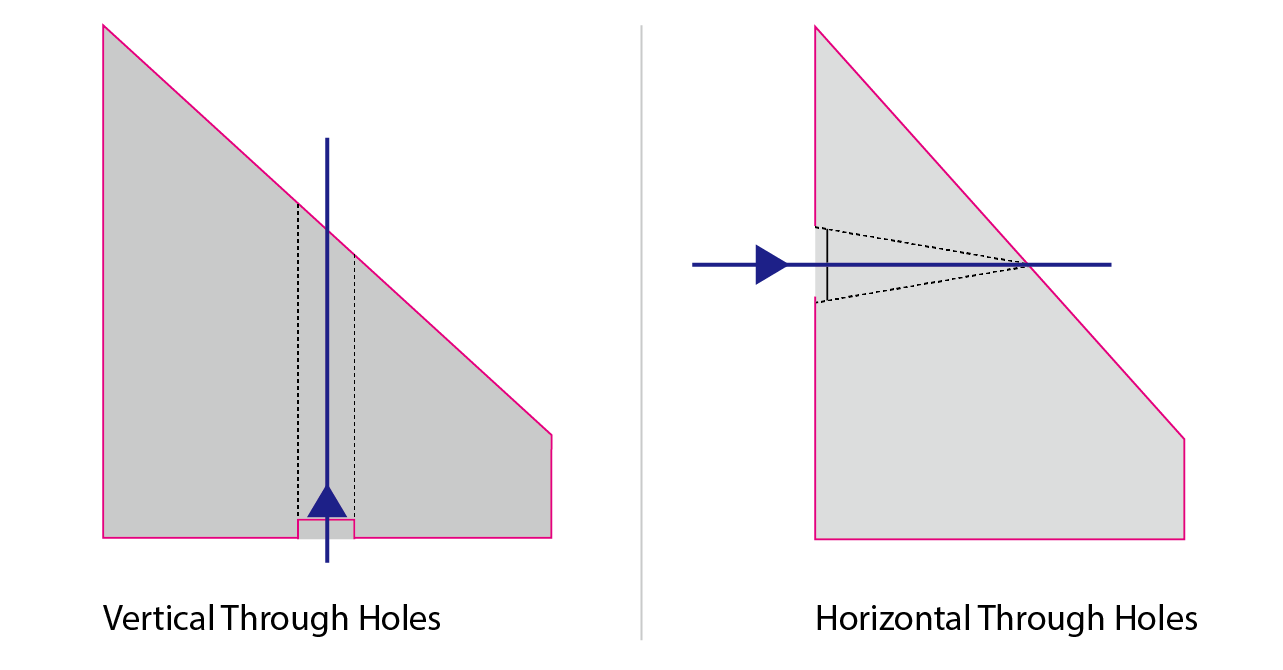
Through Holes on Offaxis Parabolic MirrorWhen you need two beams of light to travel along the same path, you can use off-axis parabolic mirrors with holes in the middle. These mirrors have a curved surface that can bend and focus light without making it blurry. The hole lets one beam go through while the other beam bounces off the surface and meets at a point away from the mirror. This way, you can avoid blocking or interfering with the beam. |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Limitations of Off Axis Parabolic Mirrors (OAP)
|
Off axis parabolic mirror (OAP) is one of the common components to build terahertz and infrared light paths. Based on the principle of geometry paraboloid, off-axis mirror can focus the collimated beam / collimated THz wave with parallel incidence to the focus, and can also convert the terahertz wave or infrared light emitted by point light source into parallel transmission beam.
Main applications of off-axis parabolic mirrors are as follows:
– Target simulators
– Collimators
– MTF measuring systems and other optics test devices
– Spectroscopic and FTIR systems
– Radiometers
– Beam expanders
– Laser divergence measuring systems
Use of off-axis optics allows optical engineers to achieve the following advantages:
– Minimize system sizes
– Minimize system weight
– Both “wedged” and equal-thick mirrors are available
– Minimize system cost
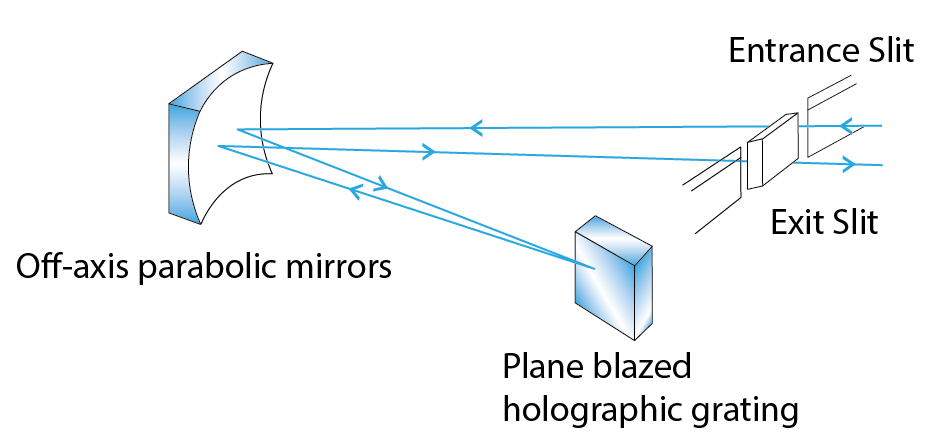
OAP in Czemy-Turner SpectrometerA Czerny-Turner spectrometer is a type of imaging spectrometer that uses a plane grating and two spherical mirrors to resolve spectral intensity. It is based on a coma-free geometry that satisfies the Shafer equation. A Czerny-Turner spectrometer can be used for various measurement techniques, such as atomic emission, absorption, reflection and fluorescence spectroscopy. It offers good resolution and sensing length, and can be used to spectrally resolve atomic emission lines. However, it also suffers from some drawbacks, such as keystone distortion due to astigmatism, stray light due to multiple reflections, and low light throughput due to narrow slits. |
 |
OAP in Littrow Type SpectrometerA Littrow type spectrometer is a type of spectrometer that uses a plane reflection grating and a spherical mirror to disperse and focus light. It is based on a configuration that minimises deviation and maximises dispersion by having the incident light enter at the Brewster angle. A Littrow type spectrometer can be used for various measurement techniques, such as atomic emission, absorption, reflection and fluorescence spectroscopy. It offers good spectral resolution and low astigmatism, but it also suffers from some drawbacks, such as low light throughput due to narrow slits, stray light due to multiple reflections, and limited wavelength range due to fixed grating angle |
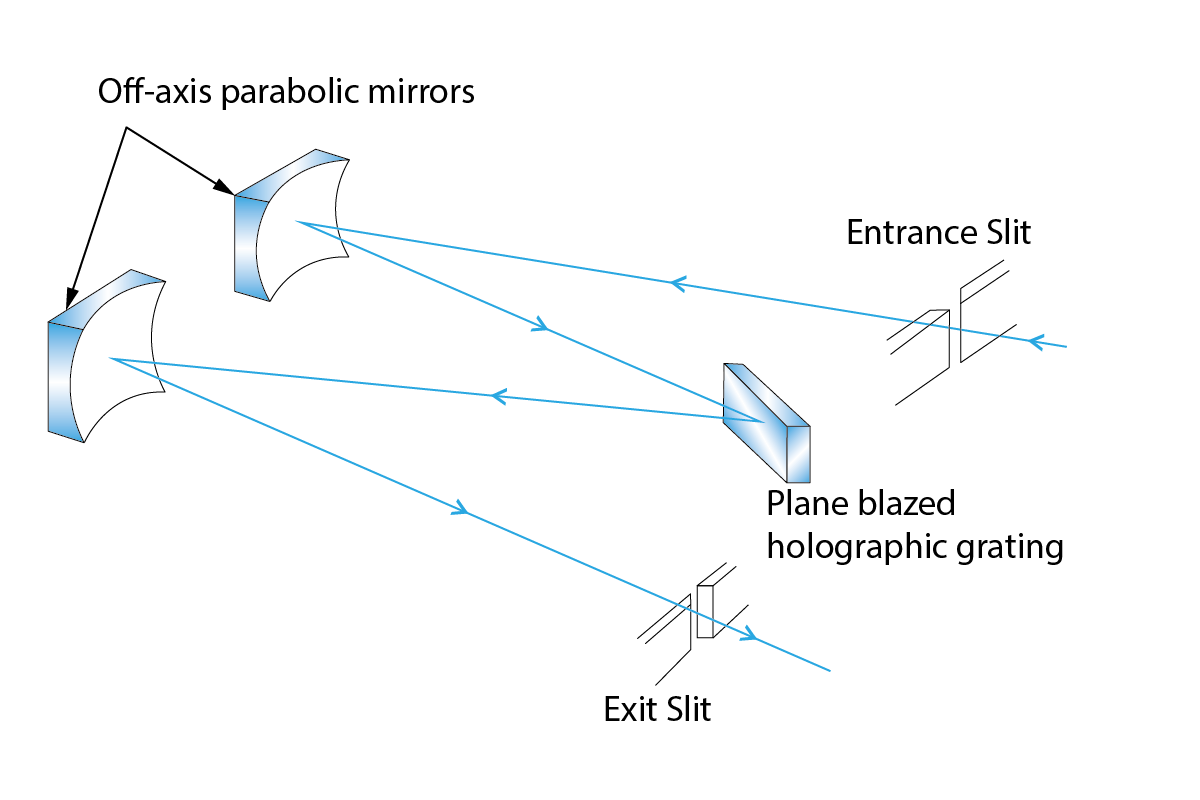 |
Below are some previously made configurations for OAPs, and you can go to the coating curve tab for checking relevant coating options.
| wdt_ID | SKU | Diameter(mm) | PRICE(USD) | Coating | Off Axis Angle | EFL,PFL(mm) | Leadtime & MOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OAP.127 | 12.7 | 95 | Protected Gold,Protected Silver,UV-Ehanced Aluminum,Protected Aluminum | 15,30,45,60,90 | Upon Design | 1week & 10pcs |
| 2 | OAP.254 | 25.4 | 179 | Protected Gold,Protected Silver,UV-Ehanced Aluminum,Protected Aluminum | 15,30,45,60,90 | Upon Design | 1week & 10pcs |
| 3 | OAP.504 | 50.4 | 342 | Protected Gold,Protected Silver,UV-Ehanced Aluminum,Protected Aluminum | 15,30,45,60,90 | Upon Design | 1week & 10pcs |
Off axis parabolic mirror Drawing (General) >
*Through Holes is available for all OAPs and upon requests.
*Typical Value for RFL(mm) = 12.7,25.4,50.8,76.2 / Accordingly PFL(mm) = 6.35,12.7,25.4,38.1
Protective Gold Coating
UV Enhanced Aluminum Coating
Protective Silver Coating
Large Off Axis Parabolic MirrorsSZLASER also offer large off parabolic mirrors (up to 6inches). These large OAPs are generally much more expensive than smaller ones, and it requires customization. |
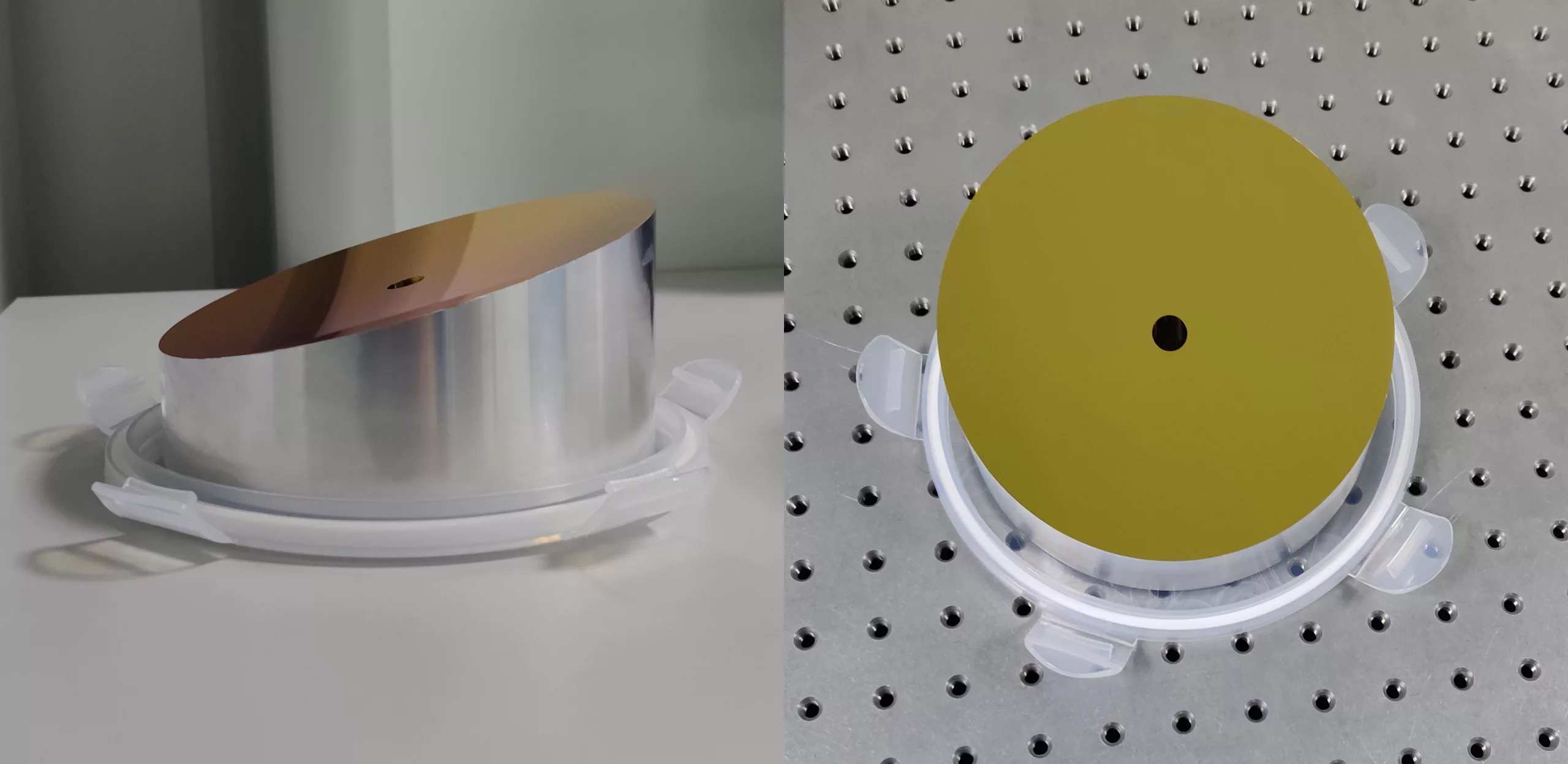 6inch Large OAP 30° |
OAP fundamentals
A parabolic mirror takes light from a point source located at the focus and creates a collimated beam. In other words, a source with spherical wavefronts placed at the parabolic focus is converted into a beam with plane wavefronts. The reverse operation is also true; plane wavefronts incident on the parabolic mirror are focused at the focal point. This is a valuable tool for optical design because the single surface of an OAP can produce a diffraction limited image without chromatic effects. A complete parabolic mirror would focus a collimated beam at its focal point, which is often not useful because it overlaps with part of the incoming beam. Accessing the focal point can be difficult and even impossible without obstructing part of the incoming beam. However, if only a portion of the parabolic surface is used, the beam will focus off-axis at a more accessible location