Dichroic Mirrors
Dichroic mirrors are color filters that selectively pass light of a small range of wavelengths while reflecting other wavelengths. They are based on the principle of thin-film interference, where alternating layers of optical coatings with different refractive indices produce phased reflections that reinforce or cancel certain wavelengths of light. Dichroic mirrors are widely used in laser, microscopy, spectroscopy, and lighting applications.
- Dichroic mirrors are color filters based on thin-film interference
- Dichroic mirrors can have different properties at different wavelengths
- Dichroic mirrors can produce or separate colors, or reflect or pass heat
- Dichroic mirrors are made of dielectric or semiconductor layers
What is a dichroic mirror
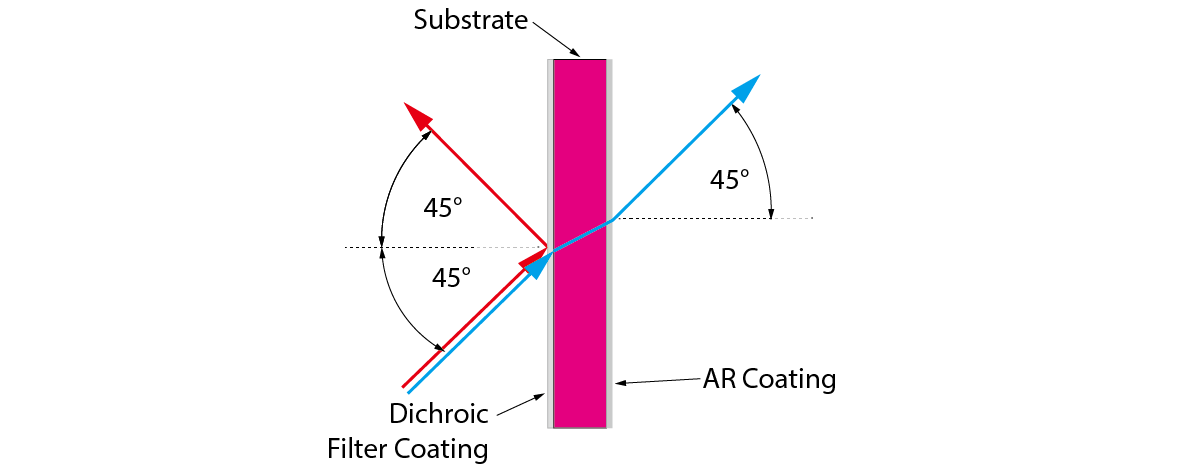
A dichroic mirror is a mirror that can reflect light of certain wavelengths (colors) while transmitting light of other wavelengths. It works by using the same principle of thin-film interference as a dichroic filter, but with a different orientation of the layers. Instead of having the layers parallel to the incident light, a dichroic mirror has the layers at an angle to the incident light. This way, the reflected light is directed to a different direction than the transmitted light.
[HERE INSERT DICHROIC FILTER vs DICHROIC MIRROR]
Dichroic mirrors are used for various purposes, such as:
- Splitting light into different colors for imaging, projection, spectroscopy, microscopy, and lighting. For example, a dichroic prism can split white light into red, green, and blue components for recording on separate CCD arrays
- Enhancing contrast or color balance in digital projection or photography. For example, a dichroic mirror can reflect unwanted infrared or ultraviolet light while transmitting visible light
Creating iridescent color effects for art and decoration. For example, a dichroic glass can produce different colors when viewed from different angles or under different lighting conditions
Dichroic Mirror VS Dichroic Filter
A dichroic mirror and a dichroic filter are both color filters that use thin-film interference to selectively pass or reflect light of different wavelengths. The main difference is that a dichroic mirror is characterized by the colors of light that it reflects, while a dichroic filter is characterized by the colors of light that it passes. For example, a dichroic mirror may reflect red light and transmit blue light, while a dichroic filter may pass red light and reflect blue light. Dichroic mirrors and filters are used for various applications such as lasers, microscopy, spectroscopy and lighting.
How a Dichroic Mirror Works?
Here is a simplified illustration of a dichroic mirror that reflects blue light and transmits red and green light:
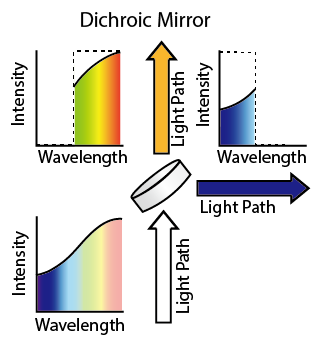
As you can see, the dichroic mirror has a thin-film coating with multiple layers of different materials on a glass substrate. The incident white light hits the coating at an angle of 45°. The blue component of the light is reflected by the coating due to constructive interference, while the red and green components are transmitted through the coating and the substrate due to destructive interference. The reflected and transmitted beams are separated by 90°
This is a basic example of how a dichroic mirror works. In reality, there may be more than two wavelength regions involved, and the coating may have more complex designs to achieve the desired spectral properties
What are some common uses of dichroic mirrors?
Some common uses of dichroic mirrors in optical, optics and lasers fields are:
- In diode-pumped lasers, dichroic mirrors can be used to inject pump light into the laser cavity while reflecting the laser light.

- In frequency-doubled lasers, dichroic mirrors can be used to couple out the harmonic light while reflecting the fundamental wave
- In fluorescence microscopy, dichroic mirrors can be used to separate the fluorescence light from the excitation light.
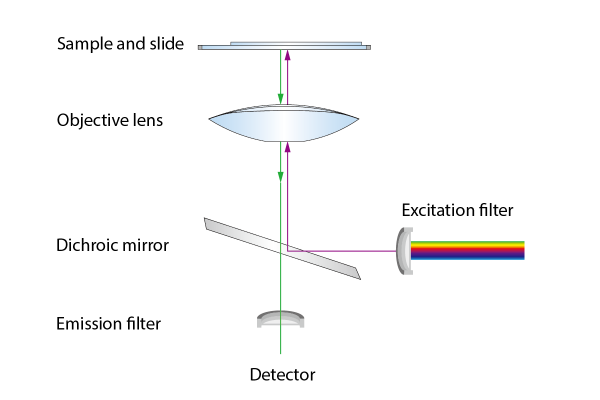
- In spectroscopy, dichroic mirrors can be used to split or combine light beams of different wavelengths for analysis
- In digital projection or photography, dichroic mirrors can be used to enhance contrast or color balance by filtering out unwanted infrared or ultraviolet light
- In art and decoration, dichroic mirrors can be used to create iridescent color effects by reflecting different colors at different angles or under different lighting conditions
Different Types of Dichroic Mirrors
Longpass Dichroic Mirrors
These mirrors reflect shorter wavelengths and transmit longer wavelengths. They can be used for laser diode pumping, fluorescence microscopy, and color separation. The specifications include the cut-on wavelength, the reflection and transmission bands, the optical density of blocking, and the angle of incidence
Shortpass Dichroic Mirrors
These mirrors reflect longer wavelengths and transmit shorter wavelengths. They can be used for laser harmonic separation, Raman spectroscopy, and color separation. The specifications include the cut-off wavelength, the reflection and transmission bands, the optical density of blocking, and the angle of incidence
Multiband Dichroic Mirrors
These mirrors have regions of reflection alternating with regions of transmission. They can be used for multicolor fluorescence microscopy, RGB projection, and color separation. The specifications include the cut-off and cut-on wavelengths for each band, the reflection and transmission bands, the optical density of blocking, and the angle of incidence



