What is optical plate?
Even though plates or blocks feature the simplest possible geometry, this type of optical component has a large number of applications. Plane-parallel plates are used as windows, for example, as protection windows for laser cavities or windows of vacuum chambers, which allow the optical access to the process zone for industrial vision purposes. Another important and widespread application for plates is their use as substrates for mirror or filter coatings or polarization layers. When arranged at the Brewster’s angle , a pure plane plate can act as polarizer, even with out any coating. Moreover, plane plates can be applied as retarders or wave plates6 when made of a birefringent optical medium such as calcite or glimmer. As shown in Figure below, a glass plate can cause parallel offset Op and longitudinal offset O1 of light rays as they pass through.
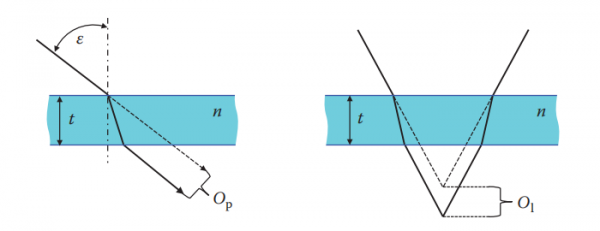
Both offsets principally depend on the thickness t and the index of refraction n of the plate material, where the amount of parallel offset is further related to the angle of incidence ε of an incident light ray at the plate’s front surface according to
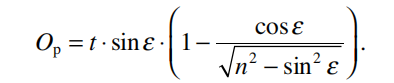
The longitudinal offset is given by
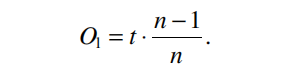
This behavior can be used for optical compensators or longitudinal or lateral displacers, for example, for shifting the image plane and realizing a defocus, respectively, in an optical system by benefiting from longitudinal offset as shown in Figure above (right).
