The frequently using optical polymer for Lens
This article introduces the optical polymer for Lens, in particular the optical properties, advantages, disadvantages and applications of PMMA.
Introduction
Optical plastics include polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polystyrene (PS), polycarbonate (PC) propyl diethylene glycol carbonate (CR39) styrene propylene copolymer (SAN) styrene acrylate copolymer In addition, it also includes some commercial products such as Optorez 1330, Zeonex E48R, etc.

PMMA
One of the most common is PMMA, also called acrylic material, which is widely used in optical lens sets. PMMA, namely polymethyl methacrylate Poly (methyl methacrylate), has excellent optical properties, comparable to optical glass. Because the refractive index and Abbe number are similar to crown glass, it is also called crown optical plastic.
Advantages
Compared with optical glass, PMMA has the advantages of simple manufacture, low cost, light weight, good impact-resistance, and good weathering and ultraviolet radiation resistance. Although unmodified pure PMMA is fragile and easy to scratch, these shortcomings can be completely solved by the modification of ingredients.
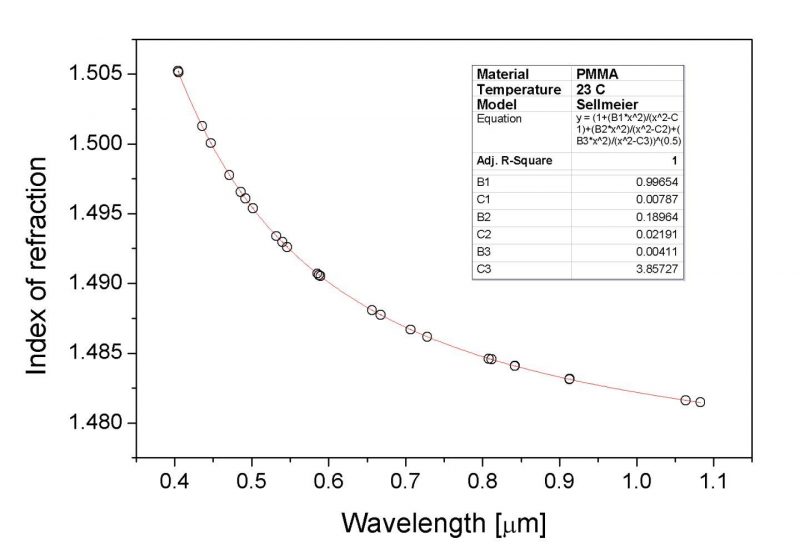
The optical lens made of PMMA has excellent optical performance. A sample with a thickness of 3mm can transmit more than 92% of visible light. The loss mainly comes from the reflection of about 4% on each side caused by the refractive index difference between the PMMA surface and the air interface. PMMA can cut off external light below 300nm, and can transmit infrared light below 2.8gm, completely cut off infrared light above 25pm, these characteristics are comparable to ordinary optical glass.
Disadvantages
The mechanical and electrical properties of PMMA are general, and the optical lenses made are easily affected by temperature. Its thermal expansion coefficient is 8~10 times that of inorganic glass, the long-term use temperature is only 80 ℃, and the material has high hygroscopicity. After soaking in water for 24 hours, the water absorption rate reaches 0.1%~0.4%. Due to the presence of easily hydrolyzed ester groups in the molecular structure, PMMA can swell and dissolve in organic solvents, while its ability to resist chemical attack is poor. However, the environmental stability of PMMA is better than most other organic polymer materials, such as polystyrene and polyethylene, so PMMA is often used in outdoor devices, and its excellent weather resistance determines that it can be exposed to sunlight even in tropical climates Over the years, the transparency and color changes remain very small.

Application
The optical properties of PMMA and the manufacturing technology of plastic components make PMMA capable of more than 80% of the optical applications of lenses. Of course, PMMA lenses are not suitable for working in environments such as high temperature and solvent contact, nor can large refractive index lenses be prepared. At present, various optical lens sets, plastic optical fibers, medical contact glasses, automotive headlights, aircraft windows, optical disc substrate materials and other fields have been widely used PMMA materials.
